Why Kidney Disease is rising in young adults
Large global studies show that early‑onset chronic kidney disease (CKD) in people aged 15–39 has risen significantly over the past three decades, even though death rates have slightly decreased. Research links this rise to lifestyle changes, rising obesity, processed diets, and better diagnostics that detect CKD earlier than before.
Important drivers in young adults:
- Earlier onset of obesity, diabetes, and hypertension, all major CKD risk factors.
- Sedentary lifestyles, high-salt and high-sugar diets, smoking, and lack of regular health check‑ups.
- Uncontrolled blood pressure–related CKD in adolescents and young adults projected to keep increasing globally up to 2035.
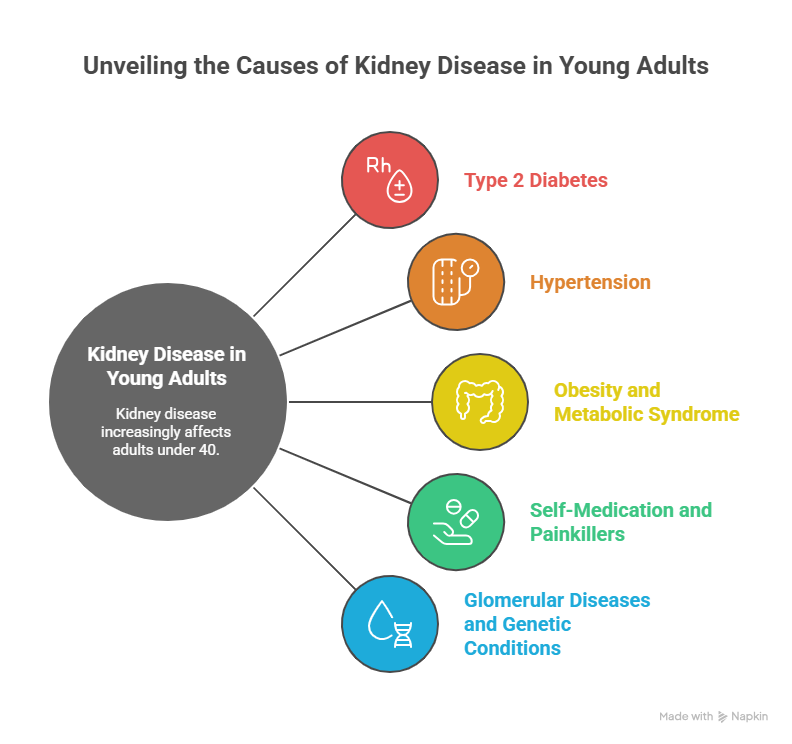
Key causes of Kidney Disease in adults in their 20s–40s
Although CKD was once seen as a disease of older people, hospitals now routinely diagnose kidney disease in adults under 40. The most common causes in this age group include:
- Type 2 diabetes: Now increasingly seen in teenagers and young professionals; persistent high blood sugar damages kidney filters (diabetic kidney disease).
- Hypertension (high BP): Often undiagnosed in young adults; long‑term high pressure injures kidney blood vessels.
- Obesity and metabolic syndrome: Central obesity, high triglycerides, and insulin resistance are strongly linked to CKD onset and faster progression.
- Self‑medication and painkillers: Frequent use of NSAIDs and some supplements can cause silent, chronic kidney damage.
- Glomerular diseases and genetic conditions: Autoimmune diseases and inherited disorders may manifest earlier in life and cause protein leakage and scarring.
These factors are often compounded by late diagnosis because early CKD usually has no symptoms; fatigue, swelling, or frothy urine appear only when damage is advanced.
Essential Kidney Health tests young adults should know
Because CKD is usually silent, proactive Kidney Health Tests are crucial, especially for anyone with diabetes, high BP, obesity, or family history. The most important tests include:
1. Blood tests
- Serum creatinine & eGFR: Measure how well kidneys filter waste; eGFR below 60 ml/min/1.73 m² for more than three months suggests CKD.
- Blood urea nitrogen (BUN): Elevated levels can indicate reduced kidney function, dehydration, or high protein breakdown.
- Electrolytes (sodium, potassium, bicarbonate): Abnormalities signal impaired kidney regulation and acid–base imbalance.
2. Urine tests
- Urine Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio (uACR): Detects micro‑albumin (small amounts of protein) leakage; >30 mg/g indicates early kidney damage, even if eGFR is still normal.
- Routine urinalysis: Looks for blood, protein, casts, or infection; persistent proteinuria or hematuria needs urgent nephrology review.
3. Imaging tests
- Renal ultrasound: Non‑invasive way to assess kidney size, structure, cysts, stones, or obstruction, often used at baseline for CKD patients.
- CT/MRI or Doppler (when needed): Used selectively to evaluate complex structural or vascular issues.
Guidelines highlight eGFR plus uACR as the two core tests every at‑risk person should do to “know your kidney numbers.”
How young adults can protect their kidney health
Good news: while lost kidney function usually cannot be completely reversed, early CKD progression can be slowed dramatically with the right habits and medical care.
Practical steps for better kidney health:
- Keep blood pressure ideally below 130/80 mmHg through salt restriction, exercise, and medicines if prescribed.
- Control blood sugar if diabetic; newer kidney‑protective drugs can slow decline.
- Maintain healthy weight, avoid crash diets, and choose whole, minimally processed foods.
- Limit painkillers and over‑the‑counter supplements; never self‑medicate long term without medical advice.
- Do annual Kidney Health Tests (blood and urine) if you have risk factors or a family history.
Why consult Dr. Sandeep Kumar Garg?
For young adults and families in Delhi NCR, guidance from an experienced kidney specialist in NCR can make the difference between early control and late complications. Dr. Sandeep Kumar Garg is a senior DM‑trained nephrologist with nearly three decades of experience in chronic kidney disease, dialysis, and kidney transplantation, practising in Meerut and catering to patients across NCR. Recognized as one of the best nephrologist in Delhi NCR region, he focuses on accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment, and counselling on lifestyle changes for long‑term kidney protection.
Conclusion
The rise of Kidney Disease among young adults is a serious but preventable trend, driven largely by lifestyle diseases and delayed testing; regular Kidney Health Tests, early risk control, and specialist care are essential to protect long‑term health.
Get a kidney health check-up now.
Contact Dr. Sandeep Kumar Garg Today!
📞 For Appointments: +91 9927600666 | 📞 For Enquiries: +91 9675600666


